Phishing attacks are on a rise in the crypto world. In this article, we will discuss five different types of Phishing attacks and how they are used by bad actors as well as how to prevent such attacks.
Fake Customer Support Phishing
The most common type of phishing is a fake customer support approach where attackers pretend to be a part of a customer support team and request information such as email, seed phrase and password. Scammers will be using similar usernames, images and will almost look identical to real customer support teams. Users seeking help from customer support become the main target for phishers, hence it is important to follow the instructions displayed on official sites and media. Most importantly customer support will never attempt to contact you first and they will never send you links or ask you for private information. When you get contacted in this manner immediately report the user and block them to stop the attack. You can always reach out to your exchange support team to verify if any requests are genuine.
Social Media Phishing
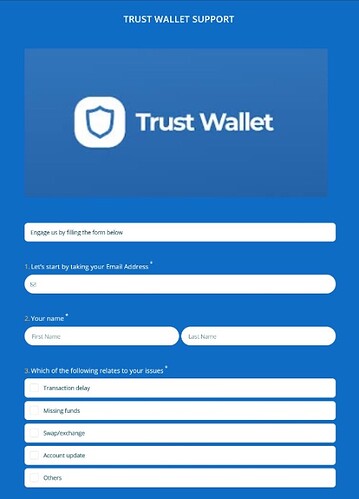
Trust Wallet users have recently been victims of targeted Twitter phishing attacks by pushing fake technical support forms. The recent phenomenon has been spotted by Lawrence Abrams who had been tracking a Twitter phishing scammer targeting Trust Wallet and Metamask users. Phishers respond to users’ tweets pretending to be from the Trust Wallet support team, who link them to phishing sites docs.google.com or forms.app links to fill out a support form and receive help.
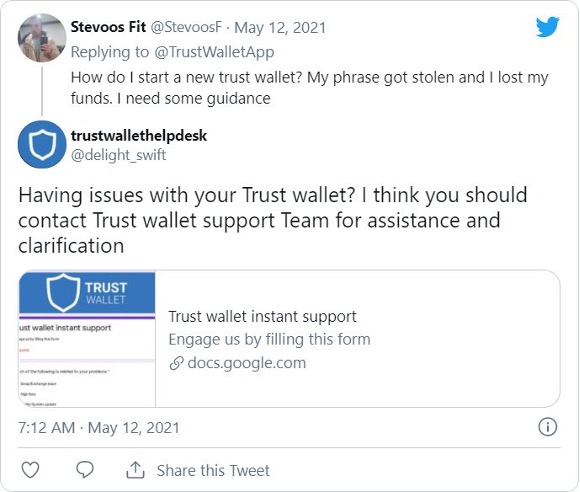
When users visit these links, they will be shown a page pretending to be a support form for Trust Wallet.
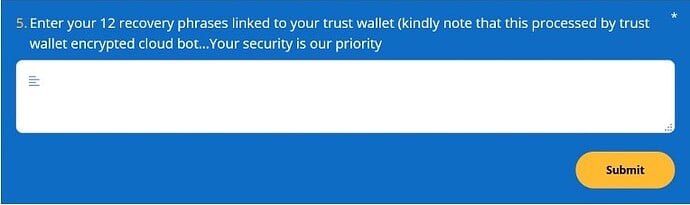
However, this will not be an ordinary form to fill as it will be asking you for your private information and most importantly your seed (recovery) phrase. We remind you never to share your seed phrase with anyone. This is the key to your coins.
These types of forms are made to steal your crypto funds. Make sure not to submit any information and report this site straight away.
SEO or Imposter Website Phishing
Scammers create a clone version of an original website; hence it is extremely hard to detect. These websites are more common to be the top hit on search using google and other engines found google Ads so that users do not suspect anything and enter sensitive information. Luckily, it is quite easy to spot fake sites. Simply check the URL of the website you intend to visit. Cloned websites will use similar-looking but different letters such as “0” instead of “o” or “ä” instead of “a” as shown below. Most importantly, bookmark the original websites that are visited frequently to reduce risk completely.
Email Phishing
Email Phishing has been around since the 1990s and it is still widely used among phishers. The aim is still to steal your funds and information by emailing you directly. The perpetrators’ emails often use well-known apps name and will have a sense of urgency using words such as “few days” “now”. These emails will often include links and the email will be written in grammatically incorrect English. Take your time to look over all the details. Check the email source and the link in the emails as it will give you an indication if the email is fake. When everything points out to a phishing email, delete the email without opening it and block the user.
Fake Mobile Apps
Mobile users are not safe from phishing. There are many fake apps on Google Play and Apple Store and many appear each day despite continuous efforts to ban them. The method appears to be particularly popular on the Android platform. There had been many users scammed with a fake Cardano wallet which had a 4.3-star rating at a time. How do you recognise a fake app? Look for obvious misspelling, often the brand colours will be incorrect on the logo and brand name. Check for how many downloads were made for this app. Popular apps have a lot more downloads. Secondly, you can always check for the publishers’ name. Most importantly use an official link from the website of the exchange or wallet to install the app.