Introduction
There are specific requirements in order to properly submit a transaction. This summarises some of the commonly asked questions about sending your Cryptocurrencies.
Reminder!
Always download the most recent version of Trust Wallet for your Android or iOS device. For a quick refresher on how to create a Multi-Coin Wallet, please go here:
How to Create a Multi-Coin Wallet
Where can I send my crypto?
With Trust Wallet, you can send your funds anywhere they are supported. In principle, a small fee will always be required in one form or another before you can make transactions. Trust Wallet does not charge any fees, this is mandated by the blockchain or the network where a token resides. Once you meet the minimum requirements, you can send them to the following:
- Cryptocurrency exchanges
- Hardware Wallets like Trezor, Ledger Nano, etc.
- Other PC, mobile and/or web wallets.
- Trust Wallet mobile app users
Important!
Always check the compatibility with the currency you are trying to send. Sending crypto is irreversible and your funds may get lost.
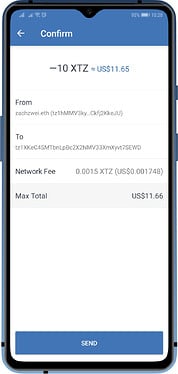
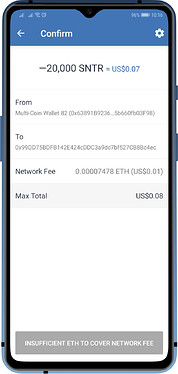
What Blockchains has fees?
Almost all of the major coins and tokens that is supported by Trust Wallet will have a certain fee deducted in order to process a transaction. The fees are not collected by your wallet, but it is given to the miners/validators.
Attention!
These coins and tokens can be transacted on their own. There will be no minimum or maximum limits, but you need to pay the fee in order to complete the transaction.
Learn more about Cryptocurrency Network Fees.
The Ethereum (ETH) Network and ERC20 tokens
During the ICO craze, anyone with an Ethereum wallet can receive these ERC20 tokens. At that time, Trust Wallet laid down its first milestone when the team added a new Wallet feature to “automagically” show any ERC20 token a user owned inside their Ethereum Wallet.
There are several ERC20-compliant tokens deployed on the Ethereum blockchain.These tokens can be used to represent various kinds of digital assets or tradable goods (such as coins, vouchers, gold certificates, loyalty points, and IOUs).
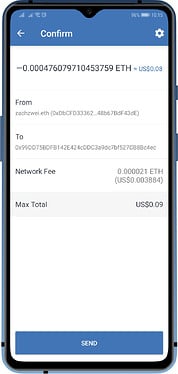
What is an ETH gas fee?
The term gas refers to the pricing mechanism used on the Ethereum network. Such a mechanism calculates the costs (fees) for performing a transaction or executing a smart contract operation.
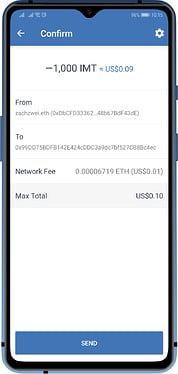
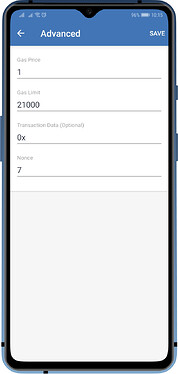
With Trust Wallet we call these gas fees as Network Fee. And since these ERC20 tokens reside on the Ethereum Network, they require a certain amount of ETH to process the transaction. Trust Wallet setup the gas prices and gas limit automatically, but in some cases, users are also able to adjust them manually, according to their needs.
Reminder!
The fees are paid to the miners. If you need your transaction to be validated quickly, you can adjust to pay a higher gas price, so that validators (miners) are incentivized to verify your transaction first than others. Similarly, setting a low gas price can cause your transaction to be stuck as miners won’t have any incentive to validate it.
Tokens on Other Blockchains
There are other blockchains similar to Ethereum where they have tokens deployed on their network. Trust Wallet has full support over these tokens too.
Binance (BNB) BEP2 Tokens
Tron (TRX) TRC10 and TRC20 Tokens
Dual Token Blockchains
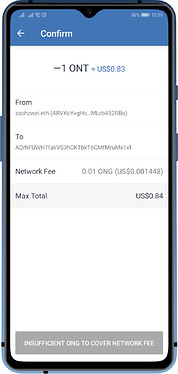
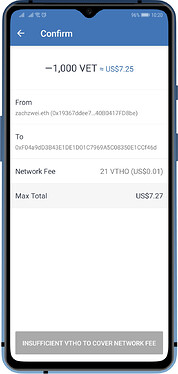
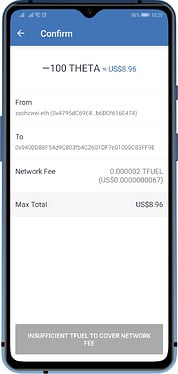
There are some blockchains that have a dual-token system. These chains generate a secondary token while you are holding them on your wallet. You can also trade them on Cryptocurrency exchanges. The secondary tokens serve as the fees on their respective chain to process transactions.
Here are the blockchains that has a dual-token system that Trust Wallet supports:
Ontology (ONT) and Ontology Gas (ONG)
Vechain (VET) and VeThor VTHO
Theta (THETA) and Theta Fuel (TFUEL)
Tokens that Require a Memo or Destination Tag
Generally speaking, a Memo or Destination Tag is almost exactly the same thing. They are used to indicate which customer to credit for the amount of the payment in that business’s own systems.
Centralized exchanges utilize this system. Rather than having tokens locked in order to activate individual addresses. See “How to Create and Activate your XRP Wallet” as an example.
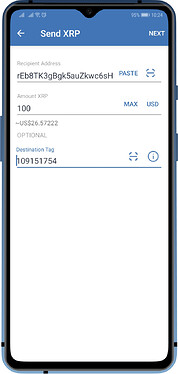
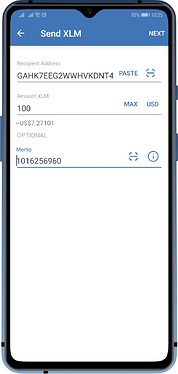
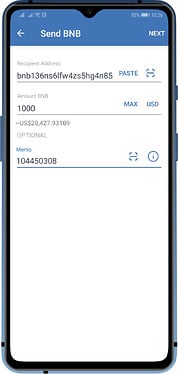
Memo (XLM, BNB) or Destination Tags (XRP) are usually composed of a bunch of numbers. Here the blockchains that require them when sending to exchanges.
Ripple (XRP)
Stellar (XLM)
Binance Coin (BNB)
Confirm before you Send
As a rule of thumb, always confirm the address of the recipient. Some exchanges/wallets will not process your deposits if the Memo or Destination Tag is missing. Sending to a Decentralized wallet does not need the use of a Memo or Destination Tag. Trust Wallet is one of the best Decentralized wallets that you can use for free.
Warning!
Once a transaction has been sent, there is no way to revert them. Lost or Stolen funds is something that we are unable to retrieve.